Pinia
1. pinia
1.1【准备一个效果】
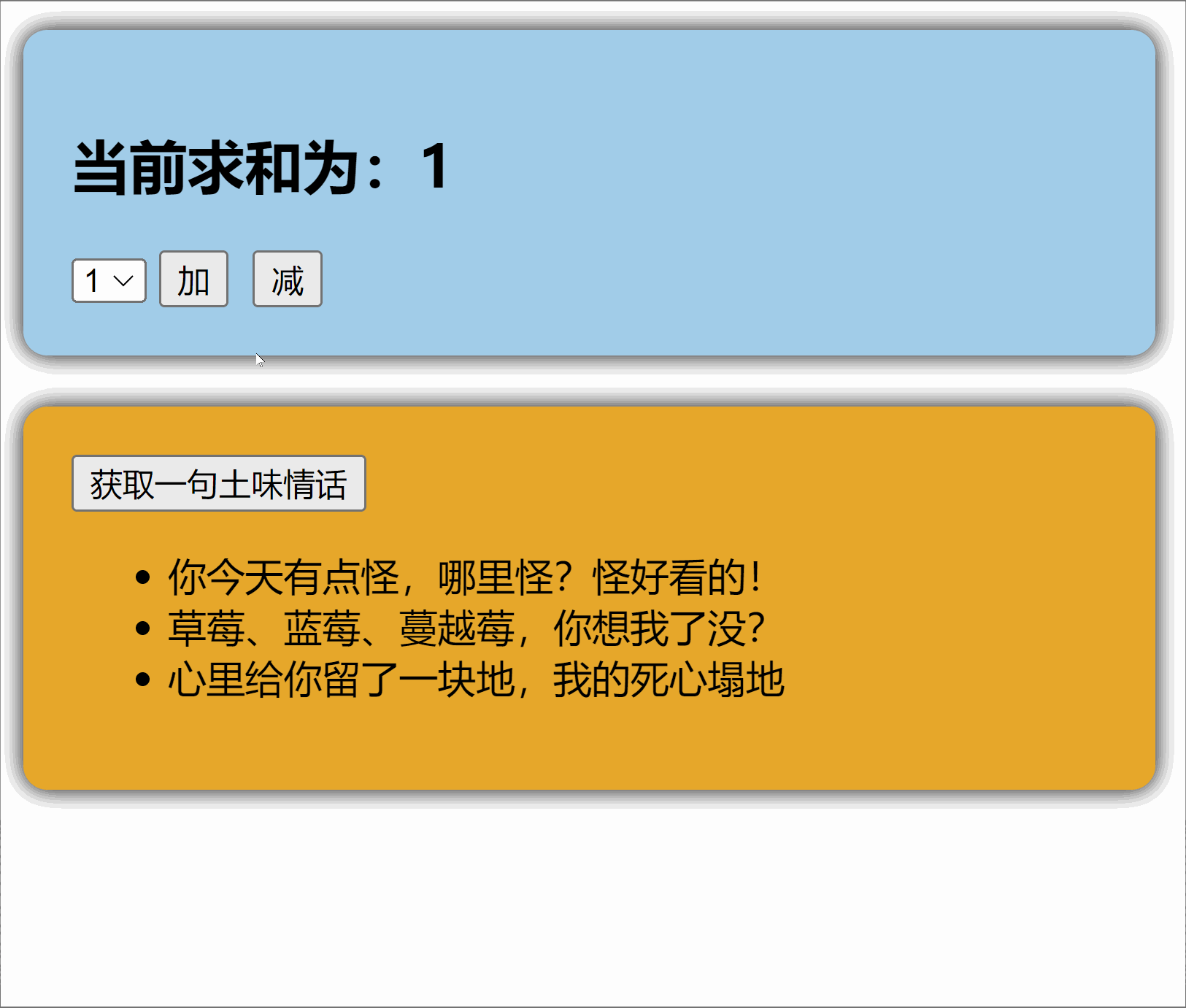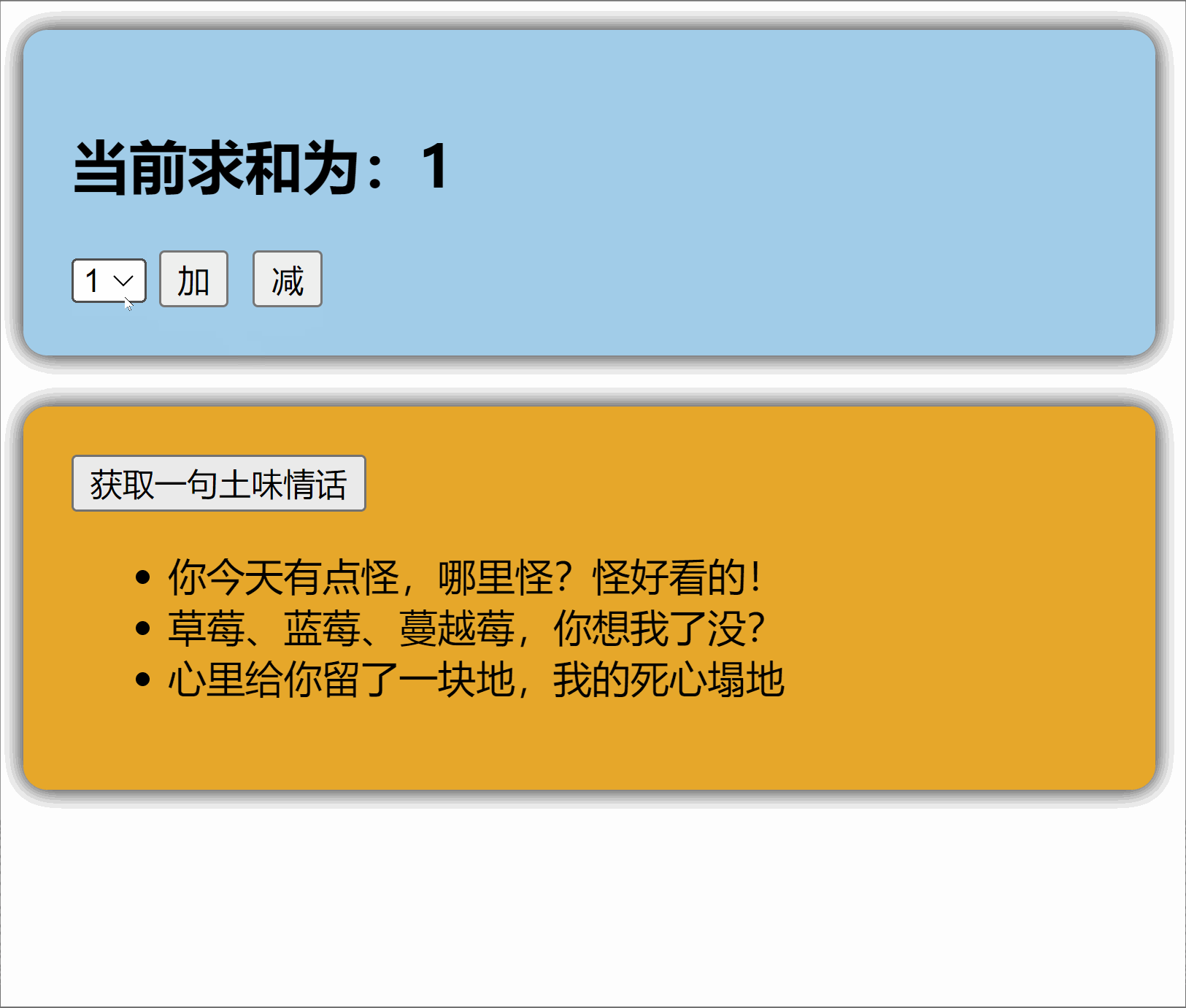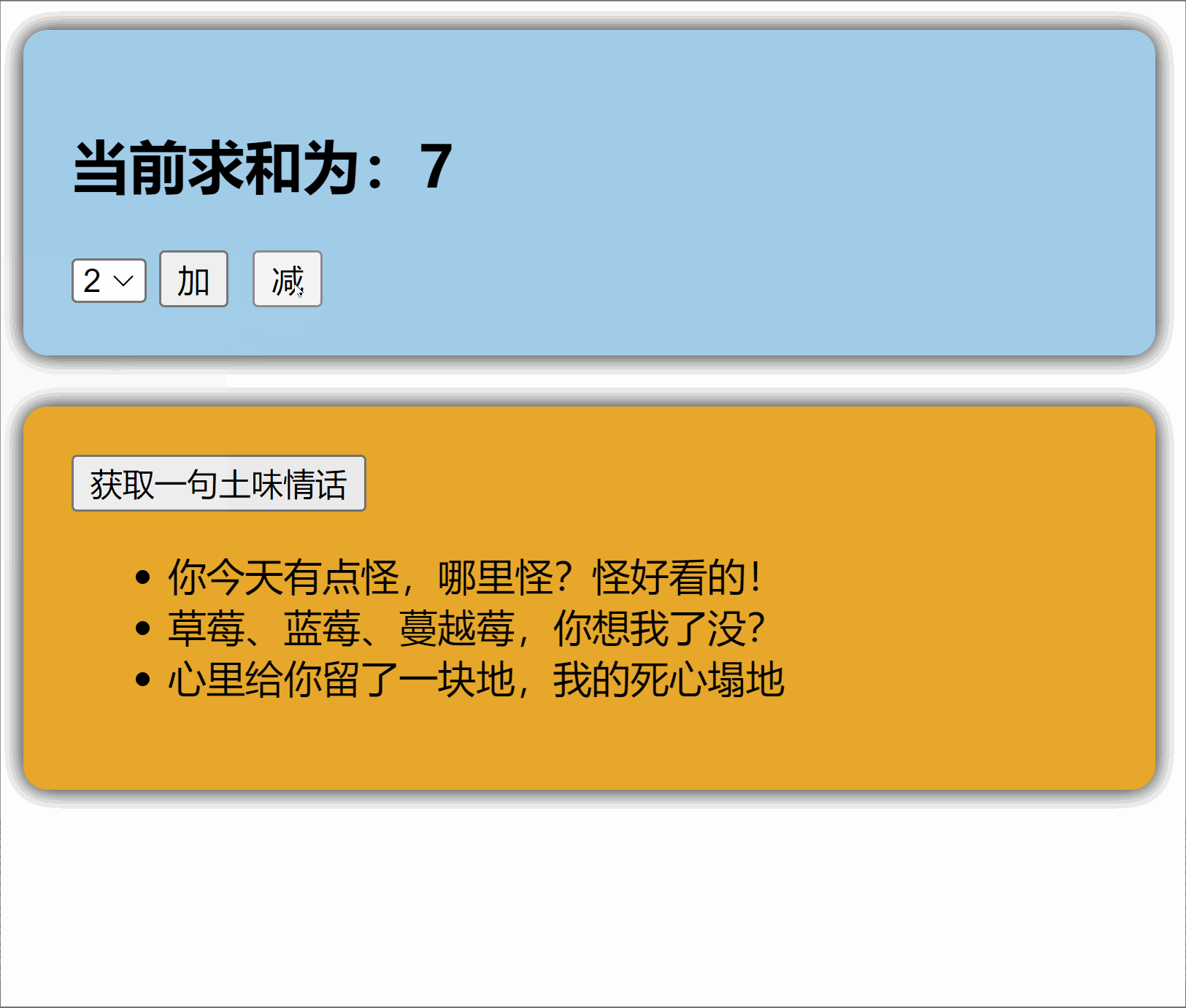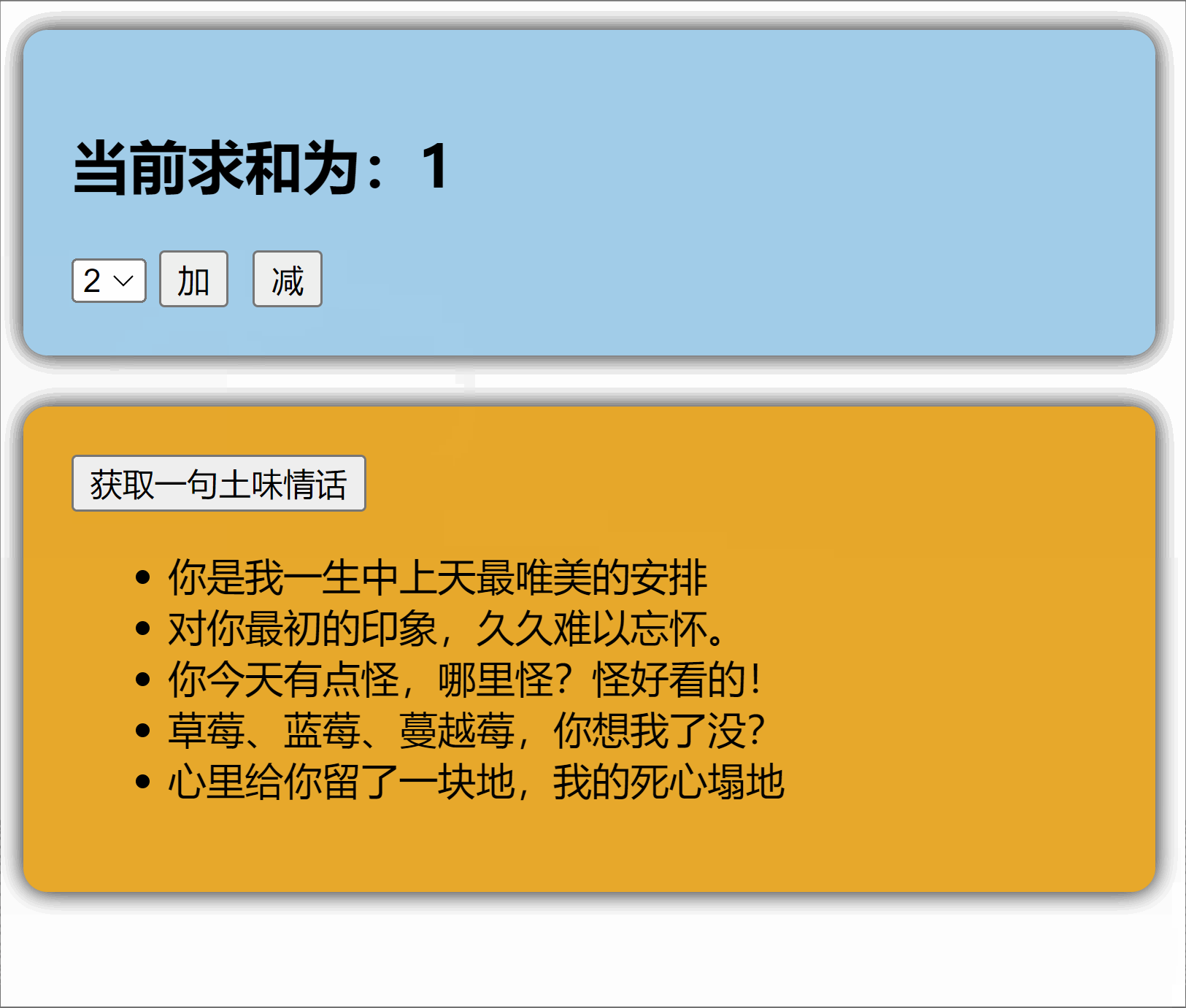
1.2【搭建 pinia 环境】
第一步:npm install pinia
第二步:操作src/main.ts
1 | import { createApp } from 'vue' |
此时开发者工具中已经有了pinia选项
1.3【存储+读取数据】
Store是一个保存:状态、业务逻辑 的实体,每个组件都可以读取、写入它。它有三个概念:
state、getter、action,相当于组件中的:data、computed和methods。具体编码:
src/store/count.ts1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16// 引入defineStore用于创建store
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
// 定义并暴露一个store
export const useCountStore = defineStore('count',{
// 动作
actions:{},
// 状态
state(){
return {
sum:6
}
},
// 计算
getters:{}
})具体编码:
src/store/talk.ts1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20// 引入defineStore用于创建store
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
// 定义并暴露一个store
export const useTalkStore = defineStore('talk',{
// 动作
actions:{},
// 状态
state(){
return {
talkList:[
{id:'yuysada01',content:'你今天有点怪,哪里怪?怪好看的!'},
{id:'yuysada02',content:'草莓、蓝莓、蔓越莓,你想我了没?'},
{id:'yuysada03',content:'心里给你留了一块地,我的死心塌地'}
]
}
},
// 计算
getters:{}
})组件中使用
state中的数据1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11<template>
<h2>当前求和为:{{ sumStore.sum }}</h2>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="Count">
// 引入对应的useXxxxxStore
import {useSumStore} from '@/store/sum'
// 调用useXxxxxStore得到对应的store
const sumStore = useSumStore()
</script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14<template>
<ul>
<li v-for="talk in talkStore.talkList" :key="talk.id">
{{ talk.content }}
</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="Count">
import axios from 'axios'
import {useTalkStore} from '@/store/talk'
const talkStore = useTalkStore()
</script>
1.4.【修改数据】(三种方式)
第一种修改方式,直接修改
1
countStore.sum = 666
第二种修改方式:批量修改
1
2
3
4countStore.$patch({
sum:999,
school:'atguigu'
})第三种修改方式:借助
action修改(action中可以编写一些业务逻辑)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useCountStore = defineStore('count', {
/*************/
actions: {
//加
increment(value:number) {
if (this.sum < 10) {
//操作countStore中的sum
this.sum += value
}
},
//减
decrement(value:number){
if(this.sum > 1){
this.sum -= value
}
}
},
/*************/
})组件中调用
action即可1
2
3
4
5// 使用countStore
const countStore = useCountStore()
// 调用对应action
countStore.incrementOdd(n.value)
1.1.【storeToRefs】
- 借助
storeToRefs将store中的数据转为ref对象,方便在模板中使用。 - 注意:
pinia提供的storeToRefs只会将数据做转换,而Vue的toRefs会转换store中数据。
1 | <template> |
1.6.【getters】
概念:当
state中的数据,需要经过处理后再使用时,可以使用getters配置。追加
getters配置。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24// 引入defineStore用于创建store
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
// 定义并暴露一个store
export const useCountStore = defineStore('count',{
// 动作
actions:{
/************/
},
// 状态
state(){
return {
sum:1,
school:'atguigu'
}
},
// 计算
getters:{
bigSum:(state):number => state.sum *10,
upperSchool():string{
return this. school.toUpperCase()
}
}
})组件中读取数据:
1
2const {increment,decrement} = countStore
let {sum,school,bigSum,upperSchool} = storeToRefs(countStore)
1.7.【$subscribe】
通过 store 的 $subscribe() 方法侦听 state 及其变化
1 | talkStore.$subscribe((mutate,state)=>{ |
1.8. 【store组合式写法】
1 | import {defineStore} from 'pinia' |
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来源 !
评论
